
Meet the Striped Hyena
The Striped Hyena (Hyaena hyaena) is an enigmatic and often-misunderstood carnivore that roams the arid and semi-arid regions of Africa, the Middle East, and the Indian subcontinent. Unlike its more famous relative, the spotted hyena, the striped hyena is solitary, elusive, and plays a crucial role in maintaining ecosystem balance.
Scientific Name: Hyaena hyaena
Phylum: Chordata
Order: Carnivora
Genus: Hyaena
Kingdom: Animalia
Class: Mammalia
Family: Hyaenidae
Species: N. Hyaena
IUCN Redlist Status:

A Striped Shadow in the Night

The striped hyena’s appearance is striking. With a shaggy grayish-brown coat marked by vertical black stripes along its body and legs, it blends perfectly into rocky landscapes and dry savannas. A mane of long hair running from head to tail stands erect when the animal feels threatened, making it appear larger to predators or rivals.
Unlike the loud and boisterous spotted hyena, the striped hyena is mostly silent, communicating through body language and occasional whoops or growls. Its large, rounded ears provide excellent hearing, allowing it to detect potential threats or food sources even in total darkness.
Where Do They hang out?
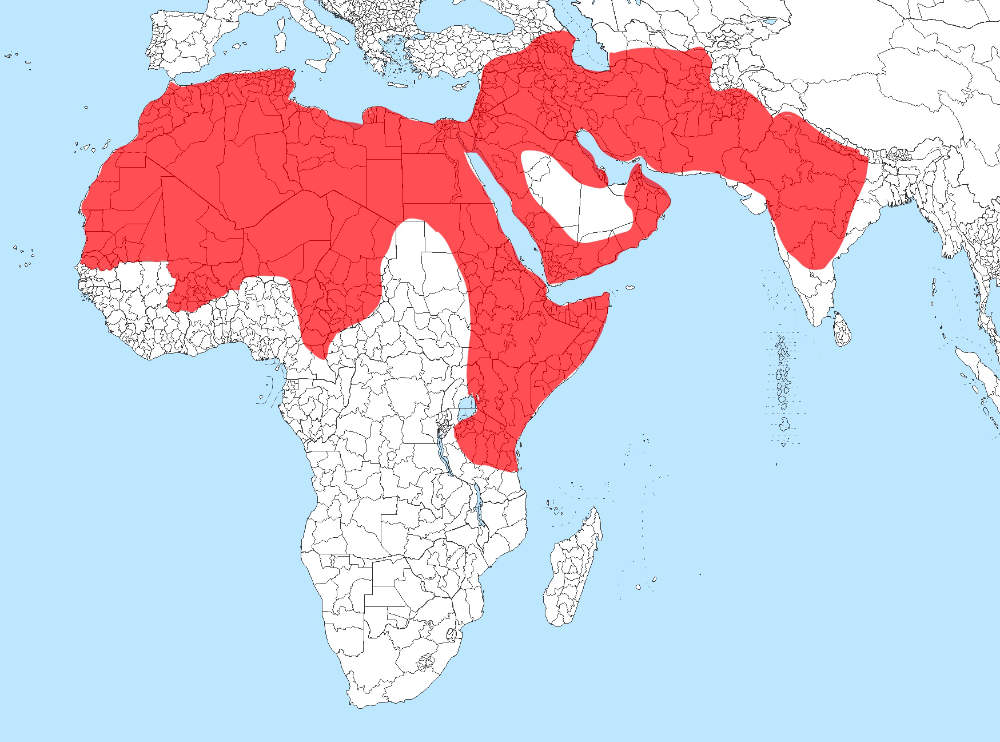
Striped hyenas inhabit a wide range of environments, from the dry African savannahs to rugged mountain slopes in the Middle East and parts of South Asia.
Countries where they are found:
Africa: Egypt, Ethiopia, Morocco, Algeria, and more
Middle East: Saudi Arabia, Israel, Iran, Yemen
Asia: India, Pakistan, Afghanistan, Nepal
Their favourite hideouts? Rocky caves, dry woodlands, and abandoned burrows, the perfect shelter for a master of disguise.
A Scavenger with a Purpose

If nature had an official clean-up crew, the striped hyena would be the team leader. Armed with one of the strongest jaw forces in the animal kingdom, it can crush bones and devour remains that other predators leave behind.
Carcasses – Nothing goes to waste! Hyenas clean up after other predators.
Small mammals, reptiles, and birds – When the opportunity arises.
Fruits and plants – A surprising addition to their diet when meat is scarce.
This bone-crunching ability not only helps them survive but also prevents disease by eliminating rotting carcasses from the environment.
Silent, Solitary, and Super Smart

Unlike their social spotted cousins, striped hyenas are primarily solitary, though they sometimes form small family units. They are nocturnal and prefer to avoid human contact. However, in some regions, they have been observed living near human settlements, feeding on garbage or livestock remains.
Striped Hyena Families

During the breeding season, males and females come together briefly. After a 90-92 day gestation period, the female gives birth to 2-4 cubs, which she raises alone in a secluded den.
5 Astonishing Facts About Striped Hyenas
Here are 5 fun facts about Hawaiian Monk Seals that you can add to your bag of information:
Silent but deadly – Unlike spotted hyenas, they don’t laugh. Instead, they communicate through subtle vocalizations and postures.
Bone crushers – Their jaws can snap bones with ease, allowing them to extract marrow that other scavengers can’t reach.
Shapeshifters – In various African and Middle Eastern cultures, striped hyenas are feared as shapeshifters,often witches or cursed individuals who transform using spells, rituals, or magical objects. By night, they become grave-robbers or predators, mimicking human voices to lure victims. Their hunched backs, eerie laughs, and scavenging habits reinforce their supernatural reputation, while iron, fire, or religious symbols are believed to ward them off. These myths explain the hyena’s strange behavior while serving as cautionary tales against dark magic.
Ancient legends – In some cultures, hyenas are linked to mythology and folklore, sometimes seen as supernatural creatures or omens.
Survivors – They have adapted to human expansion better than many other carnivores, but they still face threats from habitat loss and poaching.
Threats to their survival
Despite their ecological importance, striped hyenas face numerous threats, including:
Habitat Loss – Expanding cities, roads, and agriculture are shrinking their natural habitats.
Poaching and Retaliation – Farmers often kill hyenas to protect livestock, even though they rarely attack live animals.
Poisoning – In some areas, hyenas are deliberately poisoned due to false beliefs that they steal children or livestock.
Traffic Accidents – As they scavenge near roads, many fall victim to vehicle collisions.
How You Can Help Save the Striped Hyena
While policy changes are critical, public support is equally important. Here’s how you can contribute to pangolin conservation:
- Support conservation organizations that focus on predator protection.
- Reduce waste – Less garbage means fewer opportunities for scavengers to come into conflict with humans.
- Spread awareness – Educate others about the ecological importance of hyenas and dispel myths.
- The striped hyena may be shy and secretive, but its role in nature is undeniable. Protecting these misunderstood scavengers ensures a healthier ecosystem for all.
- Shop at Artsefact: Part of the proceeds go towards wildlife and habitat conservation.
Striped Hyena Fact sheet
Would you like a striped hyena fact sheet?
Here’s how you can gain access:
- Sign up for our newsletter for exclusive updates and wildlife conservation tips (Your welcome email has your Password for the Portal)
- Visit https://artsefact.com/factsheets/ where you can access and download ALL Factsheets

Resources
- The IUCN List of Threatened Species – https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/10274/45195080
- National Geographic – https://www.nationalgeographic.com/animals/article/hyenas-myths-lion-king-africa
- African Wildlife Foundation – https://www.awf.org/wildlife-conservation/hyena

